Tech News
We’re about to learn a whole lot more about how the human body reacts to space
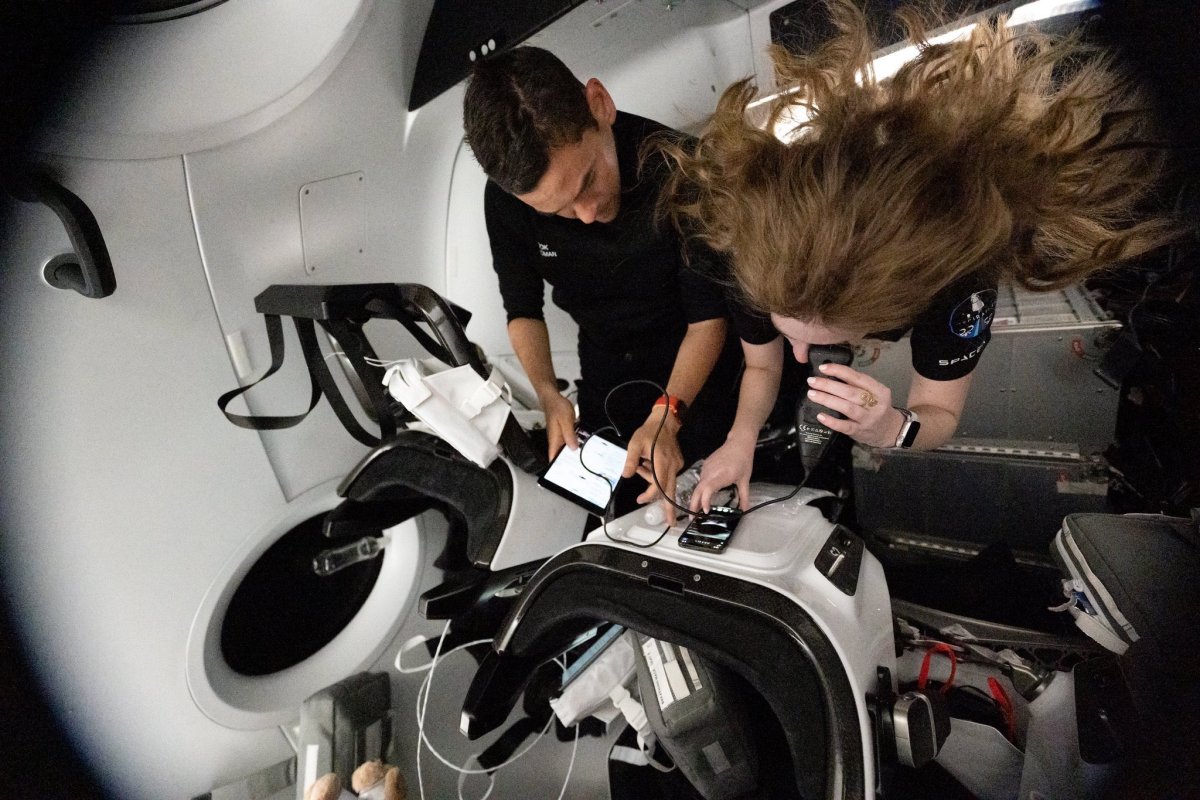

The potential for a renaissance in human spaceflight research is on the horizon, with a growing number of private citizens venturing into space and advancements in data collection techniques for studying these space travelers.
A recent publication in the journal Nature shed light on the physical and mental changes experienced by the Inspiration4 crew during their mission in partnership with SpaceX. The crew’s ability to collect and provide over 100,000 health-related data points has allowed researchers to analyze the effects of space travel on the human body.
Despite receiving extensive training from SpaceX, the Inspiration4 crew’s preparation was not as rigorous as that of NASA astronauts. However, their willingness to participate in data collection has opened up new possibilities for research in space.
The crew’s diverse backgrounds and lack of prior spaceflight experience presented a unique challenge for researchers, who had to design tests that could be easily performed with minimal training. Apple Watches and environmental sensors onboard the capsule provided additional data for correlating with the crew’s health metrics.
Efforts are underway to digitize testing and make data collection more passive to reduce the cognitive burden on private astronauts. This data will be crucial as more private citizens venture into space, allowing researchers to better understand the effects of spaceflight on a wider range of individuals.
Initial findings from the Inspiration4 mission suggest that short-duration spaceflights do not pose significant health risks, contradicting previous assumptions about the dangers of long-term space travel. Commercial spaceflight providers have shown willingness to collaborate with research institutions like TRISH to standardize and share data from their missions.
As non-governmental space missions become more common, questions arise about the ethical considerations and regulations surrounding human research in space. The role of private astronauts in advancing scientific research and their social responsibility in contributing to the knowledge base are topics of ongoing discussion.
Ultimately, the increasing interest in space tourism and the potential for more private citizens to travel to space raise important considerations for the future of human research in outer space.
She emphasized that advancements in wearable technology have alleviated the burden on research participants. This includes devices like the Apple Watch, as well as innovative technology such as the Biobutton and sweat patch, which continuously gather various vital signs.
“We want to make the process easier for you. Instead of uncomfortable procedures like needles or ultrasounds, all you need to do is wear the Biobutton and apply the sweat patch.”
-

 Breaking News2 years ago
Breaking News2 years agoCroatia to reintroduce compulsory military draft as regional tensions soar
-

 Destination1 year ago
Destination1 year agoSingapore Airlines CEO set to join board of Air India, BA News, BA
-

 Gadgets1 year ago
Gadgets1 year agoSupernatural Season 16 Revival News, Cast, Plot and Release Date
-

 Productivity2 years ago
Productivity2 years agoHow Your Contact Center Can Become A Customer Engagement Center
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoBangladeshi police agents accused of selling citizens’ personal information on Telegram
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoGoogle Pixel 9 Pro vs Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra: Camera Comparison Review
-

 Gaming2 years ago
Gaming2 years agoThe Criterion Collection announces November 2024 releases, Seven Samurai 4K and more
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoFallout Season 2 Potential Release Date, Cast, Plot and News