Gadgets
Past experiences strongly affect empathy in mice
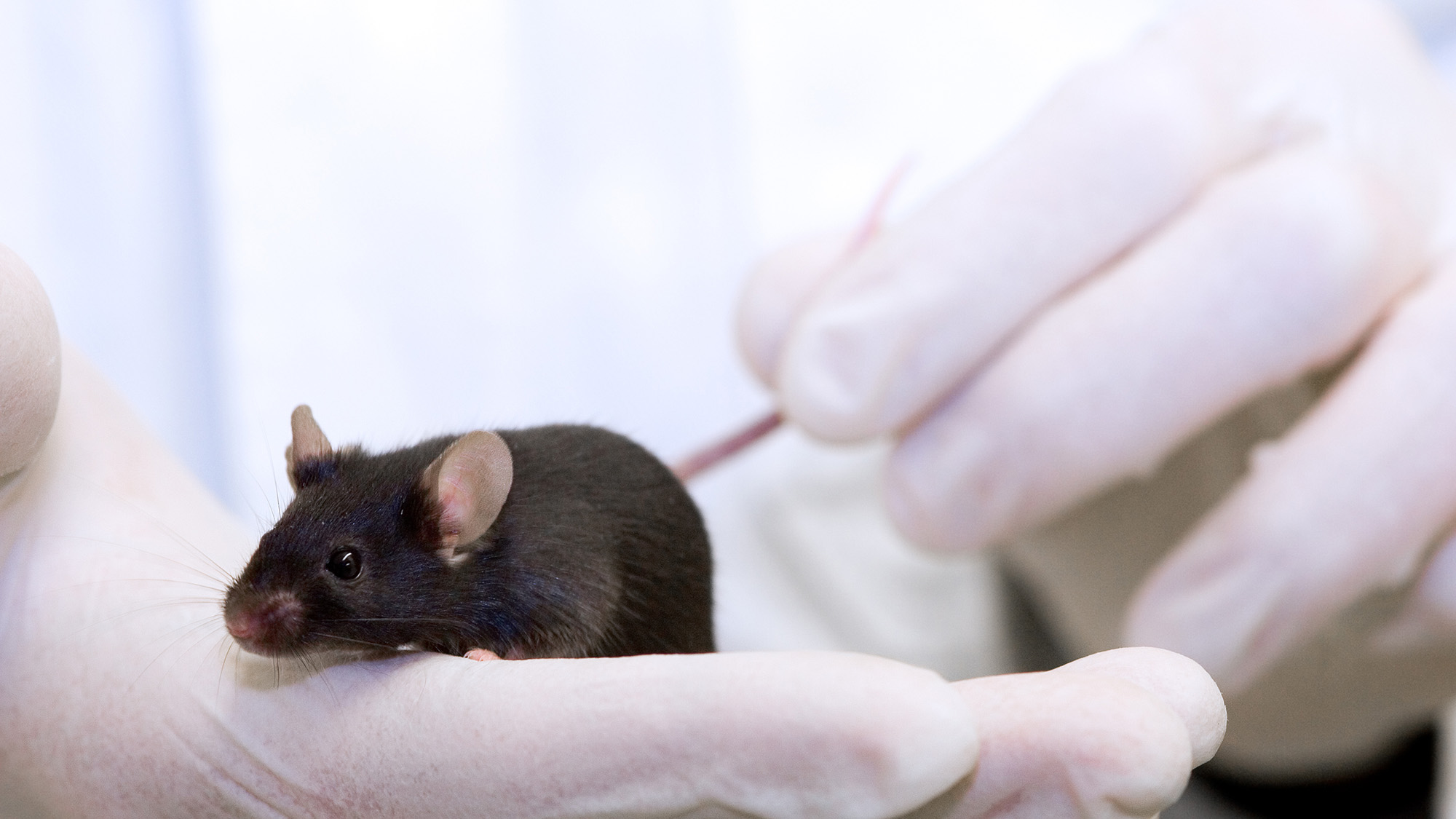
Recognizing and responding to the emotional state of others is crucial for social animals like humans. Empathy, specifically understanding when someone is in emotional distress, is a key aspect of this ability.
Individuals can have varying responses when witnessing emotional distress in others. These responses can be categorized as either prosocial, where one reaches out to provide care and comfort, or antisocial, where the distress triggers similar emotions in the witness, causing them to focus on their own feelings.
The response to emotional distress is influenced by a person’s own experiences, particularly if they have had similar encounters. A recent study published in Nature Neuroscience explores how negative self-experiences impact responses to emotional distress in others.
While the ability to recognize and react to emotions is not exclusive to humans, many other mammals also exhibit similar capabilities. The study on mice revealed that negative self-experiences did affect their responses to stressful situations in others, mirroring human empathy and suggesting similar neurological foundations.
The study found that mice with negative self-experiences tended to exhibit more avoidant behavior when witnessing distress, compared to naive mice. Hormones and social hierarchy also played a role, with dominant males showing more antisocial responses and female mice in estrus being unaffected by negative experiences.
The researchers also explored the neurological basis for these findings, focusing on the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) neurons. Inhibiting CRF activity in the mPFC increased prosocial responses in negative self-experienced mice and naive mice, highlighting the role of CRF in modulating stress responses and emotional recognition.
[ Related: How video game tech, AI, and computer vision help decode animal pain and behavior ]
The study concludes that CRF activity in the mPFC influences the recognition of stress emotions in mice. Targeting mPFC CRF neurons could potentially aid in developing therapies for psychiatric conditions affecting emotional responses. Understanding the neurocognitive basis of empathy may also lead to new treatments for conditions like PTSD, autism, and schizophrenia where empathy and emotional understanding are impaired.
Please rewrite this sentence.
-

 Breaking News2 years ago
Breaking News2 years agoCroatia to reintroduce compulsory military draft as regional tensions soar
-

 Destination1 year ago
Destination1 year agoSingapore Airlines CEO set to join board of Air India, BA News, BA
-

 Gadgets1 year ago
Gadgets1 year agoSupernatural Season 16 Revival News, Cast, Plot and Release Date
-

 Productivity2 years ago
Productivity2 years agoHow Your Contact Center Can Become A Customer Engagement Center
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoBangladeshi police agents accused of selling citizens’ personal information on Telegram
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoGoogle Pixel 9 Pro vs Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra: Camera Comparison Review
-

 Gaming2 years ago
Gaming2 years agoThe Criterion Collection announces November 2024 releases, Seven Samurai 4K and more
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoFallout Season 2 Potential Release Date, Cast, Plot and News