Gadgets
Paris preps for an AI-monitored Olympics
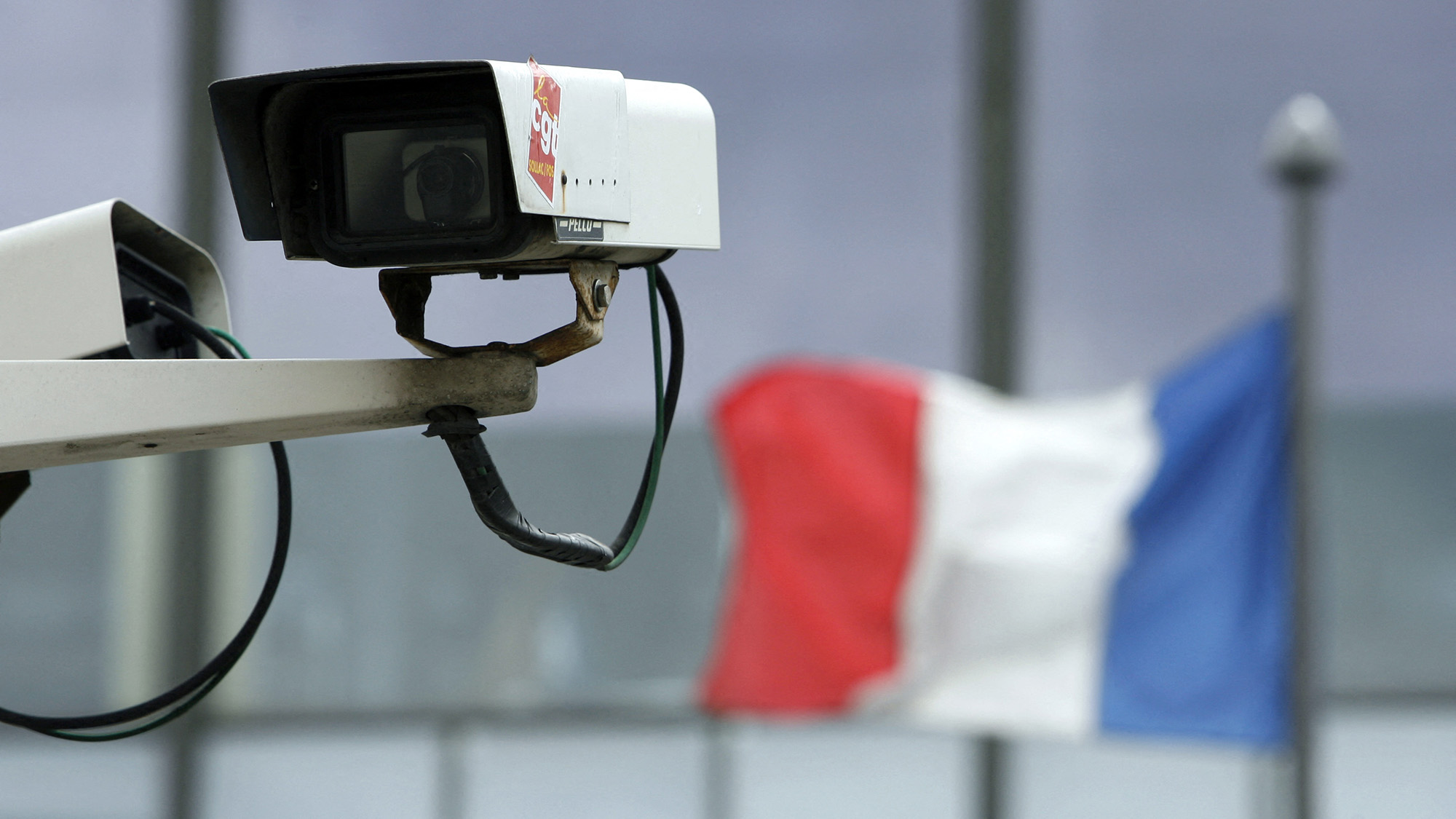

As the Summer Olympics in Paris, France approaches, nearly 100 floats carrying the world’s top athletes will glide down the Seine River, passing iconic landmarks like the Louvre and the Eiffel Tower. Amidst the half a million cheering fans, thousands of CCTV cameras will keep a watchful eye on the event in real-time. Utilizing cutting-edge artificial intelligence, these cameras will scan the crowds for any potential threats, sparking debate over privacy concerns within the European Union. This controversial AI surveillance system is just one of the many technological advancements France is implementing to ensure a highly monitored Olympic Games this year.
AI surveillance will look for crowd disturbances
Recently passed legislation in France allows law enforcement to use experimental AI algorithms to analyze public video feeds for real-time crowd monitoring. These AI models will scan footage from thousands of CCTV cameras, searching for signs of potential dangers within the Olympic crowd, such as weapons, large crowds, fights, and unattended bags.
France has partnered with tech companies like Wintics, Videtics, Orange Business, and ChapsVision to implement these AI analyses. After successful trials at subway stations, the Cannes Film Festival, and a Depeche Mode concert, Paris Police Chief Laurent Nunez has given the green light for the system’s use during the Olympics.
If the AI model detects a potential threat, it will alert a human officer for further action. French officials assure that the system will not use facial recognition or collect unique biometric identifiers, focusing instead on behavioral patterns like body movements and positioning.
French Interior Minister Gérald Darmanin emphasized that the goal is to recognize situations, not individuals, within the crowd.
Olympic games will put France’s new ‘experimental’ AI video surveillance to the test
However, critics raise concerns about the potential collection of biometric identifiers, which could violate GDPR and the EU AI Act. Civil society organizations argue that the monitoring of gait, body positions, and gestures may still be considered biometric markers, breaching GDPR rules on biometrics data collection in public spaces.
While GDPR allows exceptions for public interest, critics believe the permissions granted in France are too broad and could set a dangerous precedent for future surveillance measures. Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch warn that these surveillance powers could lead to a dystopian state and threaten civic freedoms and democratic principles.
Despite the law sunsetting in 2025, concerns remain that these measures could become permanent. Supporters argue that the security measures are necessary to prevent terrorist attacks, citing past incidents in France as justification.
As the debate continues, the world will be watching to see how France balances security and privacy during the Olympic Games.
France ramps up security for massive outdoor opening ceremony
France’s emphasis on security at this year’s Olympic Games extends beyond video surveillance. Authorities have labeled the immediate area surrounding parts of the Seine River, where the Opening Ceremonies will occur, as an “anti-terrorism perimeter.” This approximately 3.7-mile stretch will experience heightened levels of security from July 18-26.
Around 20,000 French residents residing and working within this perimeter will undergo background checks before the games to determine any potential ties to alleged Islamist extremist groups. Each individual will be issued a government-issued QR code for navigating the area during the event. Well-armed police and military units, commonly seen in Paris over the past decade, will reportedly increase tenfold. Local law enforcement will collaborate with numerous bomb disposal specialists, anti-terrorism units, and specialized forces trained to counter potential drone threats.
Throughout the years, the Olympics has been a platform for countries to showcase and implement their latest digital monitoring technologies. China notably used facial recognition at security checkpoints during the 2008 Beijing Olympics and again during recent winter games. Russian intelligence agencies overseeing the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi monitored the digital communications and internet traffic of participants and spectators. Host nations justify these expanded surveillance measures as necessary for ensuring security during times of heightened attention. While security concerns are valid, the retention of monitoring capabilities post-event has raised civil liberties issues according to activists. The potential for France to follow suit in retaining monitoring capabilities remains uncertain.
-

 Breaking News2 years ago
Breaking News2 years agoCroatia to reintroduce compulsory military draft as regional tensions soar
-

 Destination1 year ago
Destination1 year agoSingapore Airlines CEO set to join board of Air India, BA News, BA
-

 Gadgets1 year ago
Gadgets1 year agoSupernatural Season 16 Revival News, Cast, Plot and Release Date
-

 Productivity2 years ago
Productivity2 years agoHow Your Contact Center Can Become A Customer Engagement Center
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoBangladeshi police agents accused of selling citizens’ personal information on Telegram
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoGoogle Pixel 9 Pro vs Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra: Camera Comparison Review
-

 Gaming2 years ago
Gaming2 years agoThe Criterion Collection announces November 2024 releases, Seven Samurai 4K and more
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoFallout Season 2 Potential Release Date, Cast, Plot and News