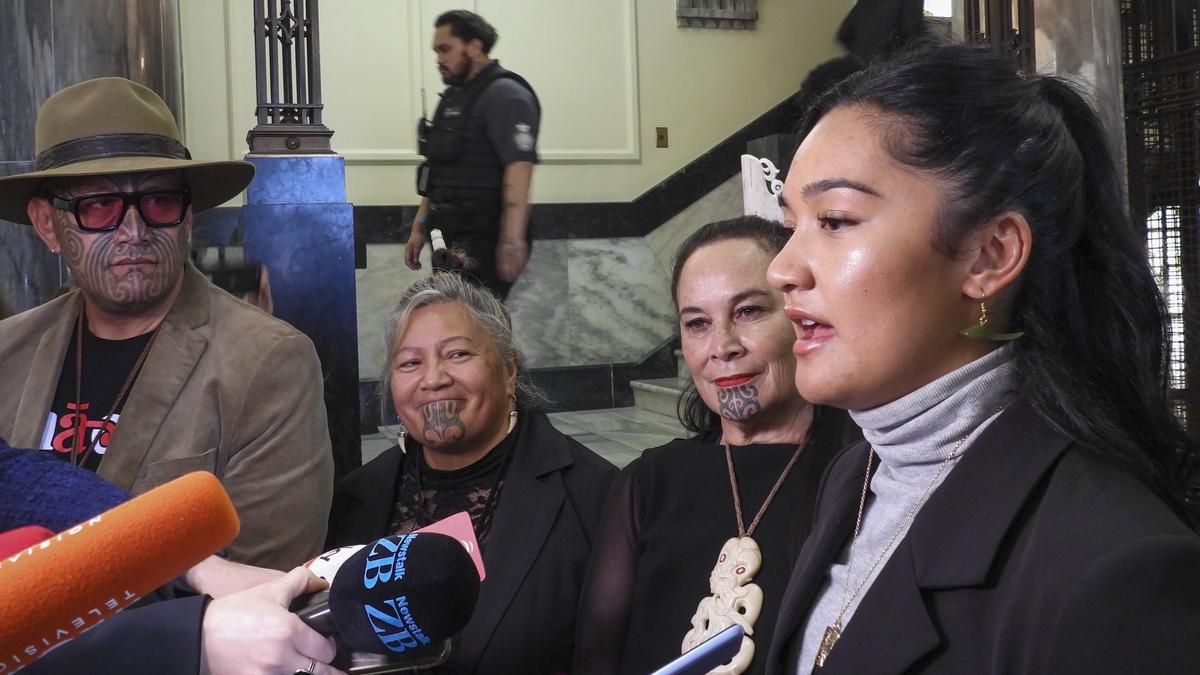A vote in New Zealand’s parliament was suspended and two lawmakers ejected on Thursday (November 14, 2024) when dramatic political theatre erupted over a controversial proposed law redefining the country’s founding agreement between Indigenous Maori and the British Crown.
Under the principles laid out in the 1840 Treaty of Waitangi, which guide the relationship between the government and Maori, tribes were promised broad rights to retain their lands and protect their interests in return for ceding governance to the British. The bill would specify that those rights should apply to all New Zealanders.
The bill has scant support and is unlikely to become law. Detractors say it threatens racial discord and constitutional upheaval, while thousands of New Zealanders are traveling the length of the country this week to protest it.
Despite its unpopularity, however, the proposed law passed its first vote on Thursday after dominating public discussion for months, due to a quirk of New Zealand’s political system that allows tiny parties to negotiate outsized influence for their agendas. It also reflects unease among some New Zealanders about more rapid progress in recent years toward upholding the promises made to Māori when the country was colonized.
Treaty of Waitangi
For decades after the Treaty of Waitangi was signed, differences between the English and Māori texts and breaches by New Zealand governments intensified the disenfranchisement of Māori.
By the middle of the 20th century, Indigenous language and culture had dwindled, much tribal land was confiscated and Māori were disadvantaged on every metric. As the Indigenous protest movement surged in the 1970s, lawmakers and the courts slowly began to elucidate what it understood the treaty to promise Māori: partnership with the Crown, participation in decision-making and protection of their interests.

“What all of these principles have in common is that they afford Māori different rights from other New Zealanders,” David Seymour, leader of minor libertarian party ACT and the bill’s author, said Thursday.
To those who have championed the treaty, that is the point. Work has involved billion-dollar land settlements, embrace of the Māori language, guaranteed representation in central and local government and attempts through policy to reverse the stark inequities Indigenous people still face.
But Mr. Seymour — who is Māori — said no law or court had actually settled for good a definition of the treaty’s principles, and that had caused division. His bill filled “a silence this parliament has left for five decades,” he said.
Prime Minister Christopher Luxon disagrees, but his party voted for the bill Thursday to fulfil the political deal with Mr. Seymour that handed Mr. Luxon power. Without enough seats to govern after last October’s election, Mr. Luxon curried support from two minor parties – including Mr. Seymour’s ACT, which won less than 9% of the vote – in return for political concessions.
Mr. Luxon told Mr. Seymour his party would vote for the treaty bill once, while promising publicly that it would go no further.
The treaty’s principles had been negotiated and debated for 184 years, Mr. Luxon told reporters Thursday, and it was “simplistic” for Mr. Seymour to suggest that they could be resolved “through the stroke of a pen”.
Opposition leaders protest
Government lawmakers made awkward speeches in parliament explaining that they opposed the bill before voting for it to jeers from opponents, who demanded they break ranks. Luxon was spared that; he left the country for the meeting of leaders from the Asia-Pacific APEC bloc hours before the vote.

His political horse-trading drew scorn from opposition lawmakers.
“Shame! Shame! Shame on you, David Seymour,” roared Willie Jackson, a veteran Māori lawmaker. “Shame on you for what you’re trying to do to this nation.”
Mr. Jackson was thrown out of the debating chamber by Speaker Gerry Brownlee for calling Mr. Seymour a liar.
“You are complicit in the harm and the division that this presents,” said Rawiri Waititi, a lawmaker from Te Pāti Māori, an Indigenous group, speaking to all who advanced the bill.
“If you vote for this bill, this is who you are,” Green party leader Chloe Swarbrick told Mr. Luxon’s lawmakers.
No one deviated from their planned votes and the bill passed. But not before one final flashpoint.
The haka
When asked how her party’s lawmakers would vote, Hana-Rawhiti Maipi-Clarke of Te Pāti Māori stood and began a ringing haka – a rhythmic Māori chant of challenge – which swelled to a roar as first opposition lawmakers, and then spectators in the public gallery, joined in.
An irate Mr. Brownlee was unable to quiet the fracas as opponents approached Mr. Seymour’s seat. The live broadcast of Parliament’s proceedings was cut and Mr. Brownlee ordered the public be removed before the vote resumed.
He suspended Ms. Maipi-Clarke, 22, from Parliament for a day.
The bill will proceed to a public submission process before another vote. Mr. Seymour hopes for an outpouring of support to change Luxon’s mind about vetoing it.
The proposal will shortly roil Parliament again. Thousands of protesters are due to arrive in the capital, Wellington, on Tuesday for what is likely to be one of the largest race relations marches in New Zealand’s history.
Published – November 15, 2024 12:00 pm IST