Gadgets
Googly-eyed potato eclipse filmed by NASA’s Perseverance rover

Phobos: The Swift Moon of Mars
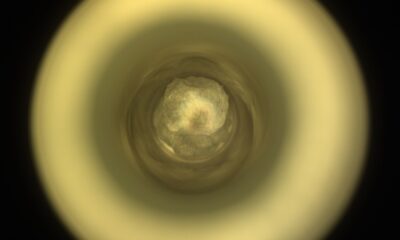
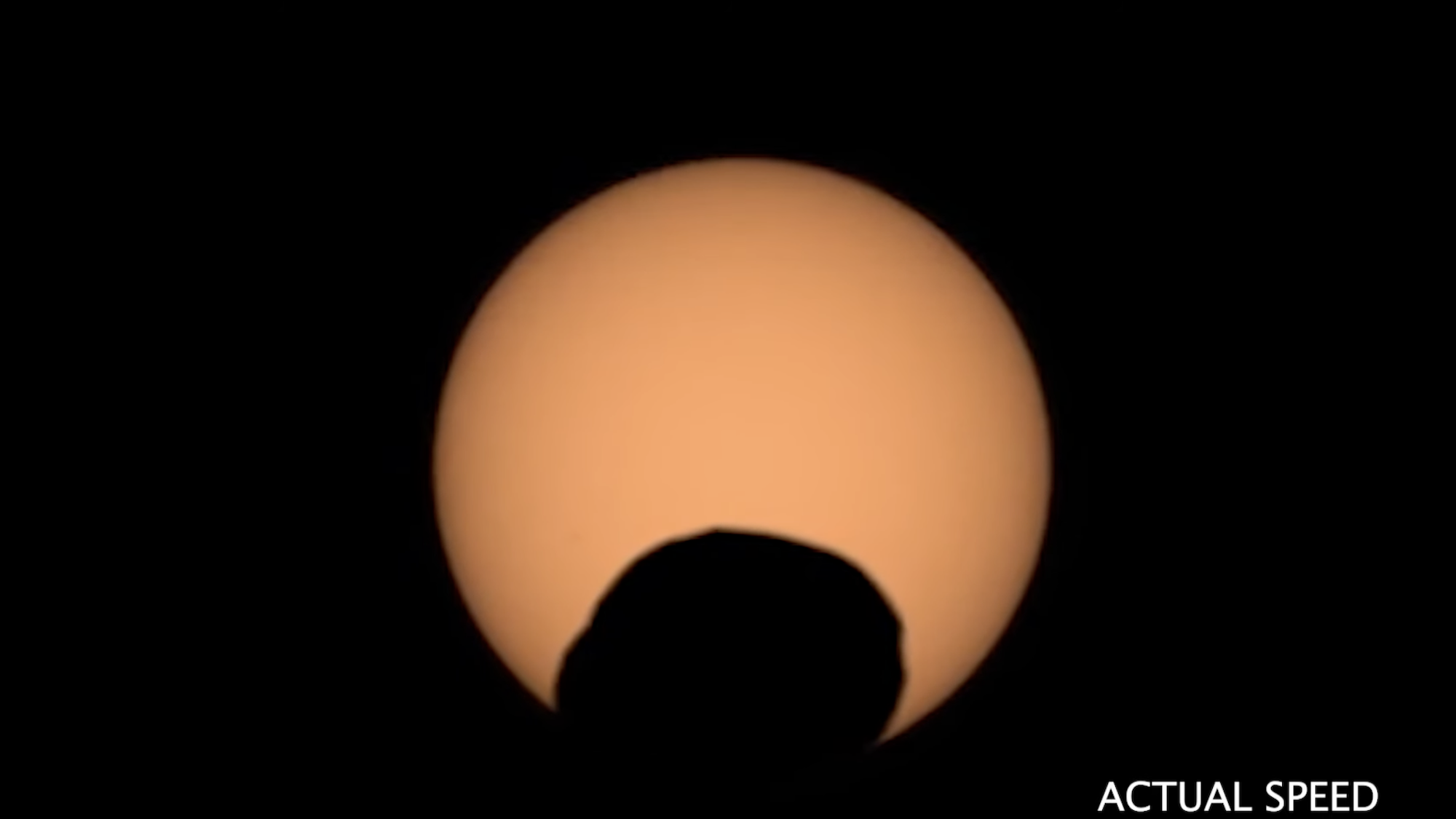
Phobos, the moon of Mars, is no slowpoke. With its small size, unique angle, and rapid orbital pattern, Phobos completes a full orbit around Mars approximately every 7.6 hours. This frequent movement increases the chances of Phobos passing in front of the Sun, creating a rare eclipse phenomenon. If you were on Mars at the right place and time, you could witness Phobos briefly turning the Sun into a giant googly eye. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover captured this incredible event in February and managed to photograph another eclipse just seven months later.
Recently, NASA showcased the latest Phobos eclipse seen on September 30th from the perspective of the Perseverance rover in Mars’ Jezero Crater. The brief eclipse lasted only 30 seconds, making Earth’s eclipses seem much longer in comparison. The footage of Phobos was captured using Perseverance’s Mastcam-Z, an instrument co-designed by Arizona State University.
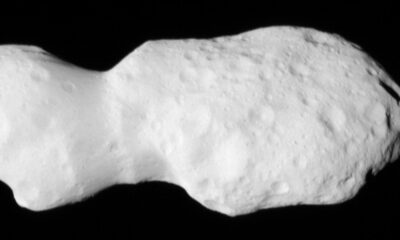
Discovered by astronomer Asaph Hall in 1877, Phobos and its companion Deimos were named after the twin Greek gods of fear and dread. The origins of these moons remain a mystery, with experts theorizing that they may have originated as captured asteroids or debris from the early Solar System formation.
[Related: A Martian solar eclipse turns the sun into a giant googly eye.]
Despite its small size of 17 miles wide, Phobos is about 157 times smaller than Earth’s moon. Both Phobos and Deimos are slowly moving closer to Mars, in contrast to Earth’s moon which is moving away from Earth. This movement suggests that the Martian moons may eventually collide with the planet or break apart to form a ring similar to Saturn’s, within the next 50 million years.
For now, there will be more opportunities for Perseverance and future human visitors to document these unique celestial events on Mars.
-

 Breaking News2 years ago
Breaking News2 years agoCroatia to reintroduce compulsory military draft as regional tensions soar
-

 Destination1 year ago
Destination1 year agoSingapore Airlines CEO set to join board of Air India, BA News, BA
-

 Gadgets1 year ago
Gadgets1 year agoSupernatural Season 16 Revival News, Cast, Plot and Release Date
-

 Productivity2 years ago
Productivity2 years agoHow Your Contact Center Can Become A Customer Engagement Center
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoBangladeshi police agents accused of selling citizens’ personal information on Telegram
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoGoogle Pixel 9 Pro vs Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra: Camera Comparison Review
-

 Gaming2 years ago
Gaming2 years agoThe Criterion Collection announces November 2024 releases, Seven Samurai 4K and more
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoFallout Season 2 Potential Release Date, Cast, Plot and News