Tech News
Watch SpaceX achieve a new record with a Falcon 9 booster
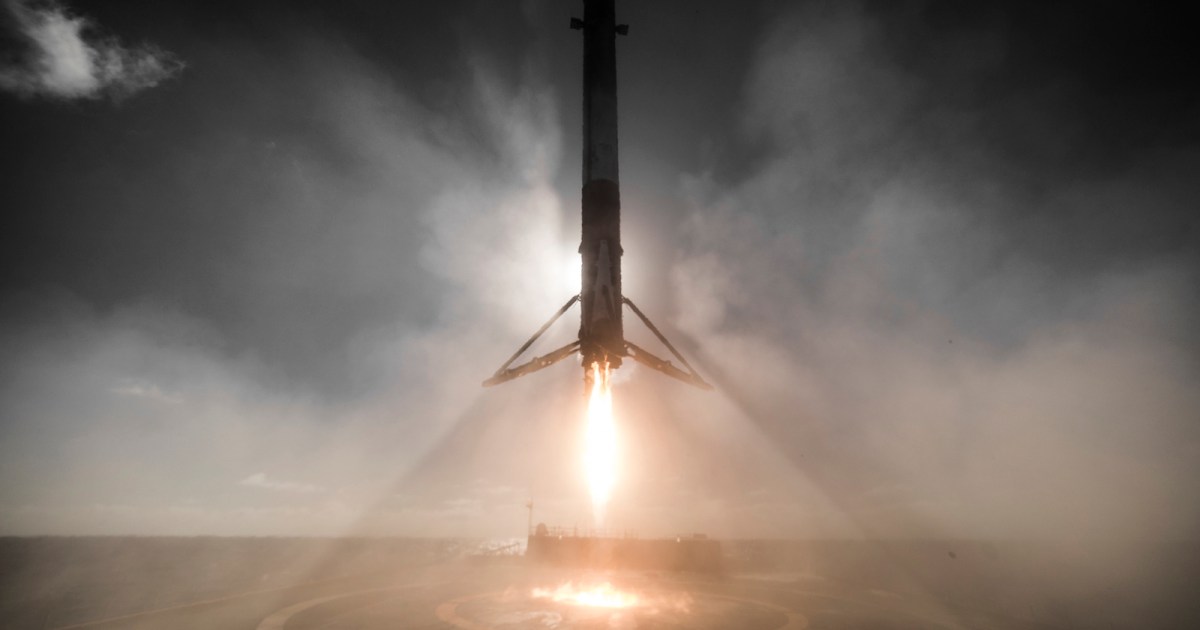

SpaceX successfully launched and landed its Falcon 9 booster for the 22nd time, setting a new record for the company.
The Falcon 9 took off from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 7:14 a.m. ET on Thursday, June 27. The rocket deployed 23 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit.
A video of the launch can be seen below:
Liftoff! pic.twitter.com/GH3FjaqbgG
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) June 27, 2024
Just eight minutes after liftoff, the Falcon 9 booster landed perfectly on a drone ship in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida.
Falcon 9 lands on the Just Read the Instructions droneship, completing the first 22nd launch and landing of a booster! pic.twitter.com/8WX1mE4QbH
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) June 27, 2024
The record-breaking booster had previously been used for various missions including launching GPS satellites, the Inspiration4 mission, and multiple Starlink missions.
The booster, known as B1062, first flew in November 2020 and had its most recent flight on May 18, 2024. Another booster, B1061, had its 21st flight on June 8, inching closer to B1062’s record. Both boosters are expected to have many more launches and landings in the future.
SpaceX’s ability to reuse rockets for multiple flights helps reduce costs and makes space more accessible for businesses and organizations looking to launch satellites or conduct research in orbit.
In addition to the Falcon 9, SpaceX is also working on its next-generation Starship rocket, which is designed for reuse and has significantly more power than the Falcon 9. The Starship has undergone several test flights, with the upcoming fifth flight test aiming to land the Super Heavy booster using a launch tower in Texas.
The successful development of the Starship will enable SpaceX to carry crew and cargo to destinations like the moon and Mars in the future.
-

 Breaking News2 years ago
Breaking News2 years agoCroatia to reintroduce compulsory military draft as regional tensions soar
-

 Destination1 year ago
Destination1 year agoSingapore Airlines CEO set to join board of Air India, BA News, BA
-

 Gadgets1 year ago
Gadgets1 year agoSupernatural Season 16 Revival News, Cast, Plot and Release Date
-

 Productivity2 years ago
Productivity2 years agoHow Your Contact Center Can Become A Customer Engagement Center
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoBangladeshi police agents accused of selling citizens’ personal information on Telegram
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoGoogle Pixel 9 Pro vs Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra: Camera Comparison Review
-

 Gaming2 years ago
Gaming2 years agoThe Criterion Collection announces November 2024 releases, Seven Samurai 4K and more
-

 Gadgets10 months ago
Gadgets10 months agoFallout Season 2 Potential Release Date, Cast, Plot and News